Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the leading Crypto Currency that emerged as an alternative to fiat currency. Bitcoin is accepted worldwide and is independent of any financial institution or country. Bitcoin is based on Block Chain technology and is generated after verifications from the network.
Bitcoin network is a distributed, decentralized, peer-to-peer ledger system. In the Bitcoin network, all users share the common ledger and any transaction is updated with all the users. This reduces the chance of errors in the transactions. After successful confirmations, a block is generated which is called Bitcoin. Bitcoin relies on the Cryptographic hash function which is secure and encrypted.

Bitcoin is also mined by the miners using hardware and software set up. Every transaction has the transaction id, hash of the previous block, and the message. To prove the transaction, several algorithms process mathematical calculations and solve the hash of the block which cannot be altered. Based on the Proof of Work, the transactions are verified. To solve for a block and add it to the block chain, two weeks time is estimated.
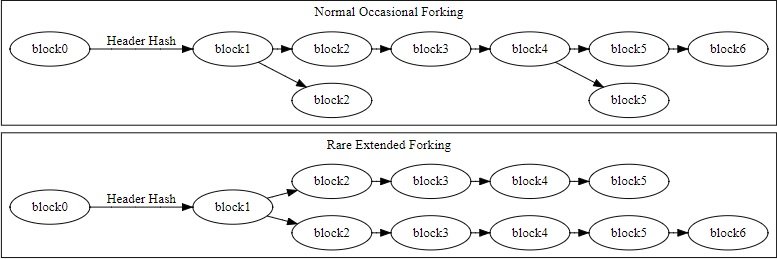
When two or more miners confirm the block at the same time, a new fork of the block chain is created. The longer side of the fork with more users is trusted by the network.
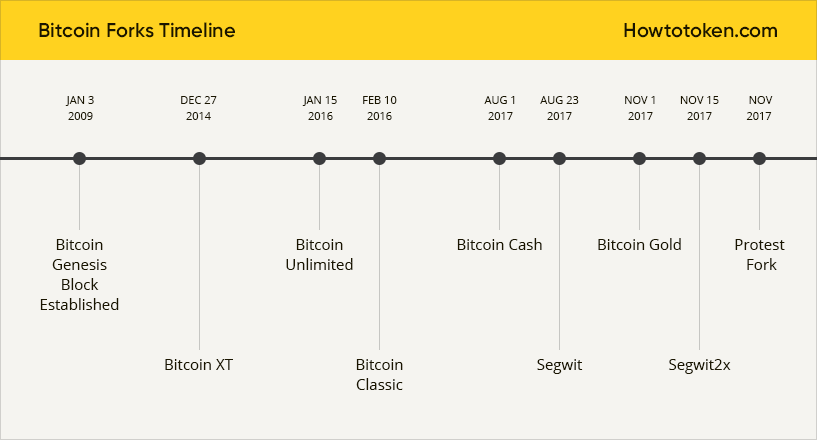
Bitcoin network runs on a common consensus agreed by all the users. When the users feel the need for a change, they will propose a fork with the changes at a future agreed block. During and after the fork, the network users may see fluctuations. Bitcoin software is highly secure and encrypted ensuring the anonymity and privacy of the users and transactions.